|
|
| ●内圧4ch,pH2ch測定と本体傾きセンサー |
![]() 食道内圧伝搬機能検査
食道内圧伝搬機能検査
食道内圧の検査は,胸のつかえ感や膨満感,嚥下困難や激しい胸痛などの症状を訴える患者に,食道の嚥下動作や蠕動がどのようにおこなわれているかを,明確に把握できる検査です。
![]()
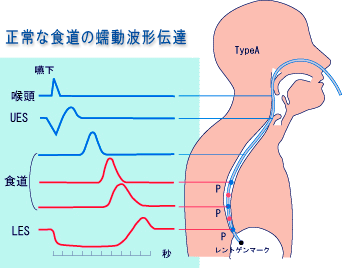
![]() 食道内圧伝搬障害の主な症例
食道内圧伝搬障害の主な症例
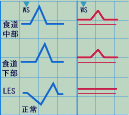
アカラシア(噴門痙攣)
LESでの弛緩が見られない。食道およびLES圧の亢進がみられ,WS時と同時に圧上昇が起こる。WSは水の嚥下のタイミング゙を示す。
GERD
食道運動機能の低下と10秒以上の一過性のLES弛緩が見られる。
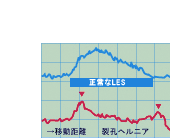
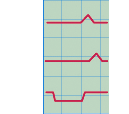
ナイトクラッカー食道
食道が異常に収縮し,普通の収縮圧はみられるが,200mmHg以上といった高い圧を示し激烈な胸痛をともなう。
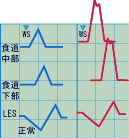
滑脱型裂孔ヘルニア
正常なLES波形に比べLES成分と食道裂孔成分が分離。LES位置のセンサーを,安静状態で引き抜きにより移動させて測定する。LESの長さも伸びている。LESは圧が15cm~30mmHgで長さ2~4cm程度が一般的。


